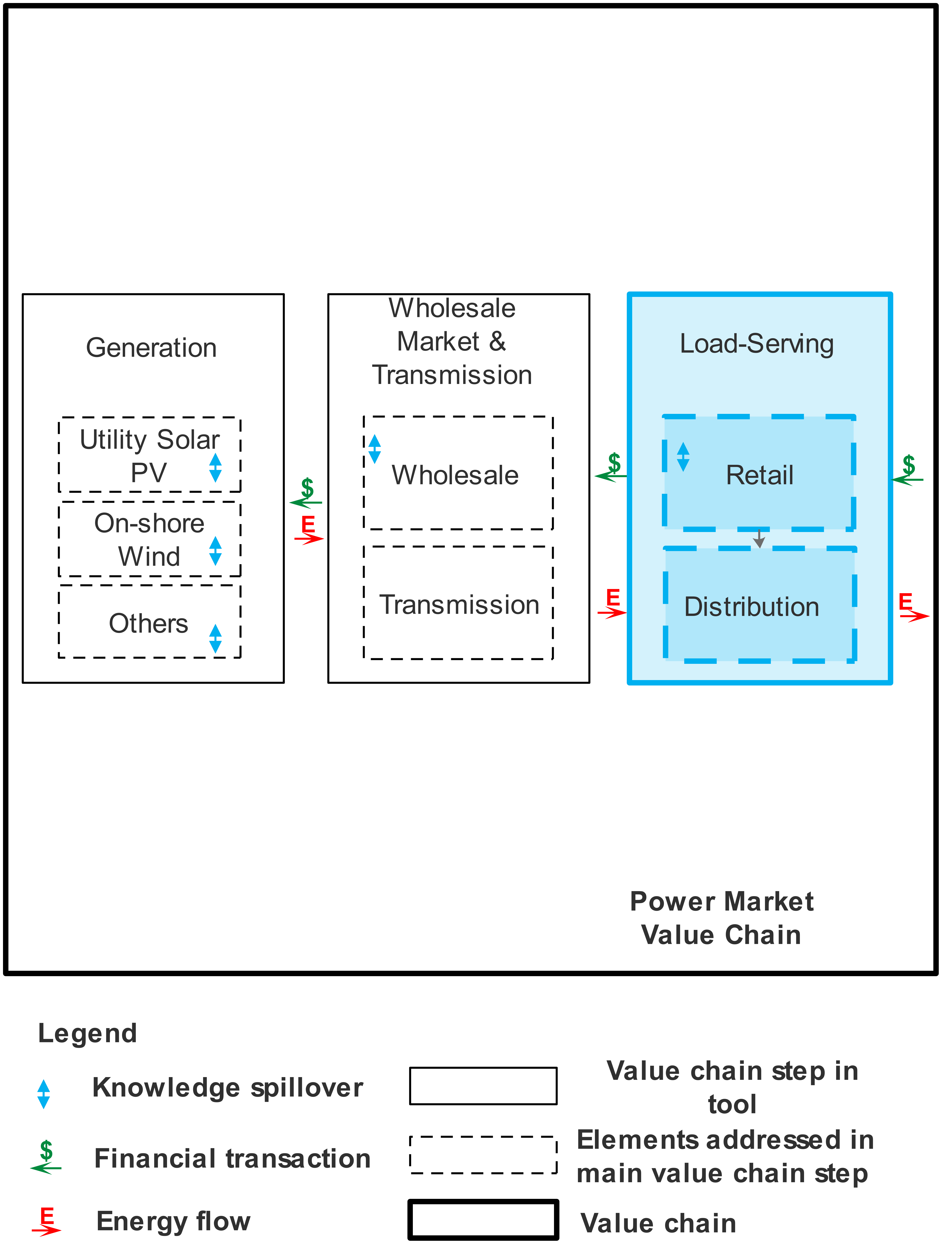
The Load Service and Distribution step of the Power Markets value chain represents the conceptual role of serving retail load and distributing electricity to end users, which might be handled by companies that only serve load, by companies that are completely vertically integrated from generation through to distribution, or by companies that pick and choose what elements of the electric power business they want to participate in. Key activities in this value chain step include aggregating load on behalf of end-use customers and making arrangements in wholesale markets to meet the aggregated load. The types of companies performing these activities include: investor-owned utilities (IOUs), publicly-owned utilities, community choice aggregators, and electric service providers. As of 2016, IOUs accounted for 60% of electricity sold, in terms of MWh. IOUs have distinct geographic territories and do not compete with one another, but are subject to direct economic regulation from a governing utility commission. While the IOU still dominates the load serving space, other types of load-serving entity (LSE) are becoming increasingly common. An increase in self- and distributed-generation also impact the demand for and nature of load service and distribution activities.
Select an information category (descriptive information, innovative outcomes, strategic conditions, and knowledge conditions) using the tabs to the left or navigate to a different value chain step using the drop-down menu at the top of the page.