Direction and Rate of Technological Change
Nacelle design innovations primarily aim to: (1) maximize efficiency, especially when operating at partial loads, (2) improve reliability (e.g., development of the direct drive concept), and (3) reduce cost through radical concept changes or more integrated design.
There are three major types of drivetrain systems: (1) geared wind turbine with double fed induction generator, (2) gearless or direct drive configuration with a synchronous generator directly attached to the main shaft and a full-power converter, and (3) hybrid configuration equipped with a gearbox and a generator coupled with a full-power converter.
One particular type of geared high-speed wind turbine with doubly fed induction generator (DFIG) configuration is currently dominating the wind industry in the United States. Under the DFIG configuration, the current in the electric generator’s rotor is controlled by a power converter; compared to other configurations, electrical losses are lower and the response to grid requirements is enhanced.
In recent years, the gearless or direct drive configuration has become more prevalent in parts of the world because of the reliability improvement by eliminating components that tend to have higher failure rates, such as gearbox bearings. There are two main types of gearless or direct drive wind turbine. The first type is based on electrically excited synchronous generators (EESGs), developed by German-based Enercon. The second type is based on permanent magnet synchronous generators (PMSGs), developed by Chinese-based Goldwind. Generally, direct drive wind turbines with PMSGs are more efficient and robust than the traditional DFIG and EESGs. However, the rare earths needed to manufacture permanent magnets have experienced substantial cost increase in the past five years, which lead to a decrease in deployment of direct drive wind turbine PMSGs, especially in Europe and the United States. As a result, the hybrid configuration – gearbox-equipped wind turbine with a full converter and squirrel cage induction generator (SCIG) – has become a compromise solution and is gaining market share in the United States. Typically, turbine configuration is strongly related to rated power. The traditional geared wind turbine with DFIG is the most popular configuration for turbines below 2 MW. In the range of 2-3 MW, hybrid configuration equipped with a gearbox and a generator coupled with a full-power converter is the preferred choice.
To help improve the reliability of a drivetrain system, Department of Energy (DOE) partners with public and private entities to develop the next generation of drivetrains that will increase reliability, decrease mass, improve efficiency and reduce cost. The advancements include single-stage gearbox, medium-speed permanent magnet generator, high-efficiency power electronics, and superconducting generators. These drivetrain design improvements are essential in reaching higher energy output as turbine components are becoming larger in size. More information on DOE’s initiative on advanced drivetrain manufacturing techniques can be found on DOE’s website. https://www.energy.gov/eere/wind/advanced-drivetrain-manufacturing
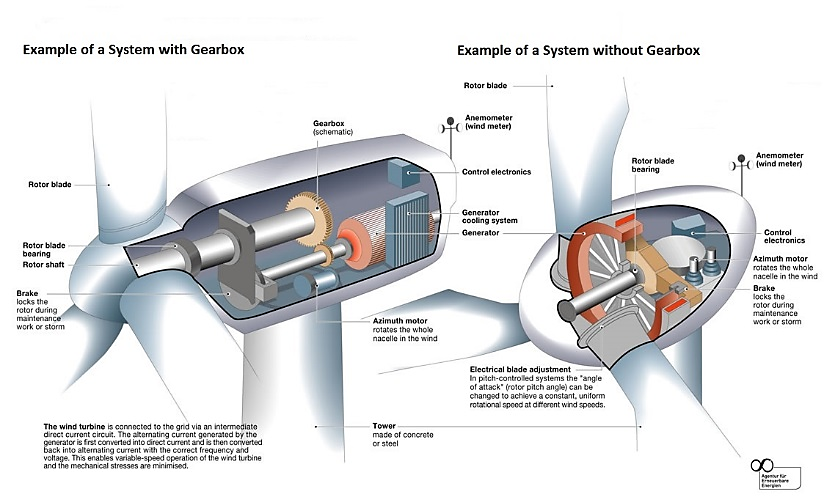
Figure IO.1 Inside of Two Types of Nacelle Systems
Source: From Green Collar Job Training website: http://www.greencollarjobtraining-free.com/index.htm
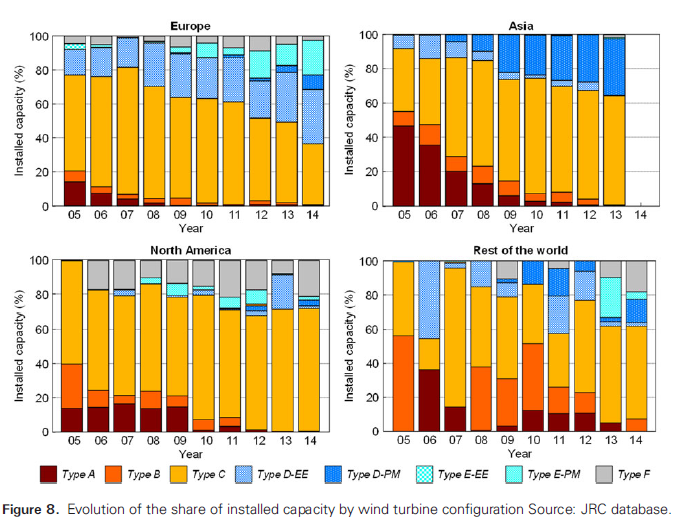
Figure IO.2 Shares of Drive Train Configuration by Region
Source: Figure 8 from Serrano-González and Lacal-Arántegui (2016). Technological evolution of onshore wind turbines—a market-based analysis. Wind Energy, 19: 2171–2187. Original data from JRC database.
Note: Type A, B, and C are geared high-speed wind turbines, in particular, type C represents the DFIG configuration. Type D-EE and type D-PM are the direct drive with EESG and PMSG, respectively. Type E-EE and type E-PM are the hybrid configuration with EESG and PMSG, respectively. Type F is the hybrid configuration with SCIG.
Data on Quantity, Cost, Quality
Table IO.1 Attributes for Learning Curve Estimation
Source: Data from Figures 12 and 20 in U.S. Department of Energy 2017 Wind Technologies Market Report
| Year | Nacelle Manufacturing Capacity (MW) |
| 1998-99 | |
| 2000-01 | |
| 2002-03 | |
| 2004-05 | |
| 2006 | 1,325 |
| 2007 | 2,825 |
| 2008 | 6,335 |
| 2009 | 5,923 |
| 2010 | 7,425 |
| 2011 | 11,885 |
| 2012 | 13,413 |
| 2013 | 12,943 |
| 2014 | 11,416 |
| 2015 | 10,218 |
| 2016 | 11,700 |
| 2017 | 11,700 |
| Source: | Figure 12 |
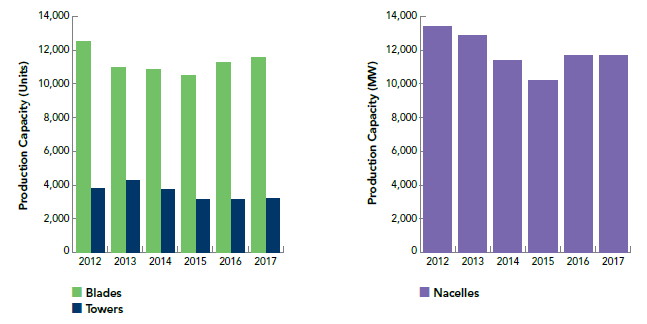
Figure IO.3 Manufacturing Production Capacity for Major Components of Towers, Blades and Nacelle
Source: Figure 84 from AWEA 2017 U.S. Wind Industry Annual Market Report Year
Additional text on quantity cost quality data
According to an industry report, the average cost of a gearbox unit is expected to decline as the wind gearbox technology has reached a higher level of maturity. The global market is dominated by independent wind gearbox manufacturers, including China High Speed Transmission Equipment, ZF Wind, and Winergy. The value of global wind gearbox market is expected to decline at a compound annual growth rate of 2.5 percent between 2016 and 2021. With improved performance and reliability, the global market of direct-drive systems grew from around 24.9 percent in 2011 to 25.2 percent in 2016 and is expected to make up to 32.1 percent of the market in 2021.